Customers are becoming less brand-loyal and have higher expectations for in-person experiences.
To address these shifts, Etisalat, a UAE telco service provider, launched EASE, the future of retail.
Global Opportunity Team
Locations included:
Etisalat (Client), Dubai
Amdocs Stakeholders, Tel Aviv
Experience Division, Texas
To address the challenges that arise from globally distributed teams, as a core project team, we implemented several strategies:
Effective Communication Tools: Utilize robust communication platforms (e.g., Slack) and video conferencing tools (e.g., Zoom, Microsoft Teams) to facilitate real-time communication and collaboration.
Regular Check-Ins: Schedule regular one-on-one and team meetings to maintain connection and alignment.
Cultural Sensitivity Training: Regularly discuss the group’s understanding of cultural differences and improve cross-cultural communication.
Clear Documentation: Maintain clear and accessible documentation for processes, projects, and decisions to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Flexible Scheduling: Be mindful of time zones and offer flexibility in scheduling meetings and deadlines.
My Role as Strategic Director
Week 0: Background Research & Team Alignment
My role involved:
Conduct market research to understand the competitive landscape and identify gaps the new service can fill.
EASE store business model.
Stakeholder expectations and requirements.
Academic study review.
Designing for technical requirements for fully autonomous stores.
Week 1: Project Kickoff
My role involved:
Facilitating known and unknown workshop sessions with Etisalat and the project team.
Industry background and market trends.
Consumer behavior is based on local culture and buying preferences.
Technical requirements based on customer and employee use cases.
Present and create presentational material and leave-behinds for the team and client.
Week 2-4: Business Requirements
My role involved:
Facilitating client workshops to define the overarching brand experience across the end-to-end customer journey.
Preliminary discussion regarding store management and maintenance.
Highlight employee training needs and automation requirements to ensure store operation runs smoothly.
Deliver the first version of store concepts based on current understanding.
Week 4-6: User Requirements
My role involved understanding users' needs, behaviors, and preferences when interacting with autonomous retail technologies. This included:
Outline the specific objectives of the research, such as understanding user expectations, identifying pain points, and evaluating usability.
Apply insights from past retail research to outline natural shopping environments, thereby understanding customer behaviors and interactions with existing retail systems.
Develop user personas that represent different types of users and their needs, goals, and pain points.
Measure users' trust in the system to securely handle their transactions and personal information.
Week 6-8: Customer Requirements
Using a new service for the first time involves thoroughly understanding customer needs, preferences, behaviors, and pain points.
My role involved:
Determine the primary questions the team needs to answer about customer requirements.
Outline specific goals, such as understanding user needs, identifying potential barriers to adoption, and gathering feedback on the service experience.
Define the characteristics and demographics of potential customers likely to use the new service.
Week 8-10: Role Play
Real-world pilot programs are crucial for understanding how users interact with the autonomous retail system. However, the team needed alternatives for retail environment observations due to our travel limitations.
My role involved:
Designing storyboards for role-play to enable the project team to explore potential behaviors and capture each interaction with digital and physical touchpoints.
Synthesize findings to inform how the technical specifications can be improved and design principles capable of meeting diverse needs.
My methodology emphasizes experiential learning, where stakeholders engage in real-world activities and apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios.
EASE RFP Response
Completing the 100+ page RFP documentation was a team effort.
In my role, I ensured the experience-related specifications were fully detailed so the business team could gauge project and building costs, resources, skillsets, and requirements.
In 10 short weeks, the team produced a comprehensive, detailed requirements document that included the concepts, UI specifications, and research artifacts I produced through participatory co-creation sessions with a cross-functional team of subject matter experts. Together, we developed a minimum viable product with just enough features to test key assumptions and gather feedback from early adopters. Applying systems thinking and service design enabled the team to predict adoption probability with a specific customer group and identify potential business risks. The risk of failure was significantly reduced by systematically testing hypotheses and validating assumptions early.
My research approach followed a framework similar to Steve Blank’s Lean Launchpad, Google’s Design Sprint, and IDEO’s Design Thinking best practices. It incorporates a scientific approach to business strategy, helping companies validate their business models, reduce risk, and build successful, customer-centric solutions. Total experience research combined with design science generated highly innovative, user-centric experiences and provided a significant competitive edge.
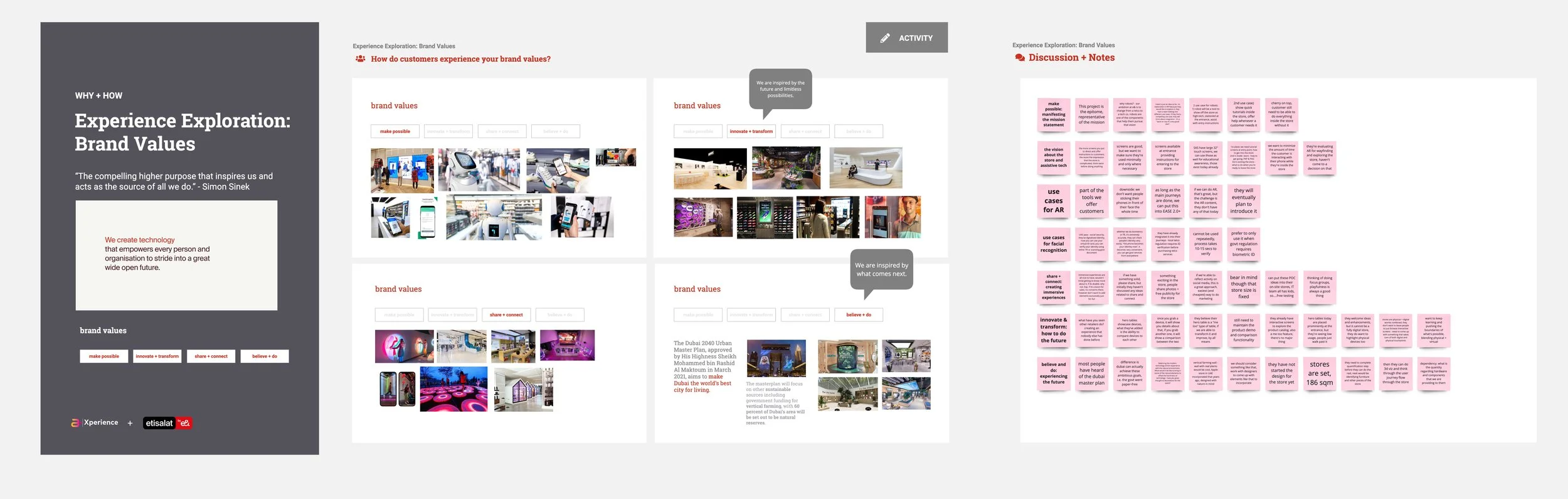
Understanding the big picture.
An ecosystem map for a fully autonomous retail store provides a holistic view of the entire system, enabling better decision-making, enhanced operational efficiency, and a superior customer experience.
Working with Edward Li, the Service Designer, I led activities to ensure the team understood how all of the store's elements contribute to the total experience.
Experience Design Methods
-
Service Blueprint
Deliver a service blueprint to communicate a clear “big picture” roadmap for achieving operational objectives. Its cross-functionality improves decision-making and helps the team understand requirements while keeping service delivery at the forefront.

-
Scenario Mapping
Support the physical store design and layout with the etisalat user experience team. Role-play scenarios for the most critical store areas: entry/exit, wayfinding, education, product placement, etc. These will be “living” documents iterated throughout the entire RFP response process.

-
Service Design Testing
A strategic plan to test working concepts and complete functionality throughout the engagement. As part of the Amdocs Experience Division, I outlined what needs to be tested, when testing starts and ends, who needs to participate in testing activities, and where testing needs to occur.

Key purpose:
Understanding Stakeholders and Relationships
Identify Stakeholders: It helps identify all stakeholders involved, including suppliers, customers, technology providers, regulatory bodies, and employees.
Visualize Relationships: It visualizes how these stakeholders interact and influence each other, highlighting dependencies and collaboration points.
Mapping Technology and Infrastructure
Technology Integration: How various technologies (e.g., AI, IoT, robotics) are integrated into the store's operations.
Infrastructure Layout: Details the physical and digital infrastructure, including sensors, cameras, payment systems, and inventory management.
Operational Workflow
Customer Journey: Outlines the customer journey from entry to exit, including touchpoints such as product selection, checkout, and customer service.
Backend Processes: Maps out backend processes like inventory management, restocking, and maintenance, ensuring efficiency and smooth operation.
Data Flow and Security
Data Collection and Usage: Illustrates how data is collected, processed, and used for decision-making, personalization, and operational efficiency.
Security Measures: Identifies potential security risks and the measures in place to protect sensitive information and ensure privacy.
Compliance and Regulation
Regulatory Requirements: Ensures all aspects of the store comply with relevant laws and regulations, including data protection, labor laws, and industry standards.
Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities
Problem Areas: Helps identify potential pain points, bottlenecks, or inefficiencies within the ecosystem.
Innovation Opportunities: Highlights areas where innovation can be applied to improve the customer experience or operational efficiency.
Strategic Planning and Development
Future Growth: Aids in planning for future growth and scalability by understanding current capabilities and identifying gaps.
Collaboration and Partnership: Facilitates better collaboration and partnerships by clearly understanding the ecosystem.
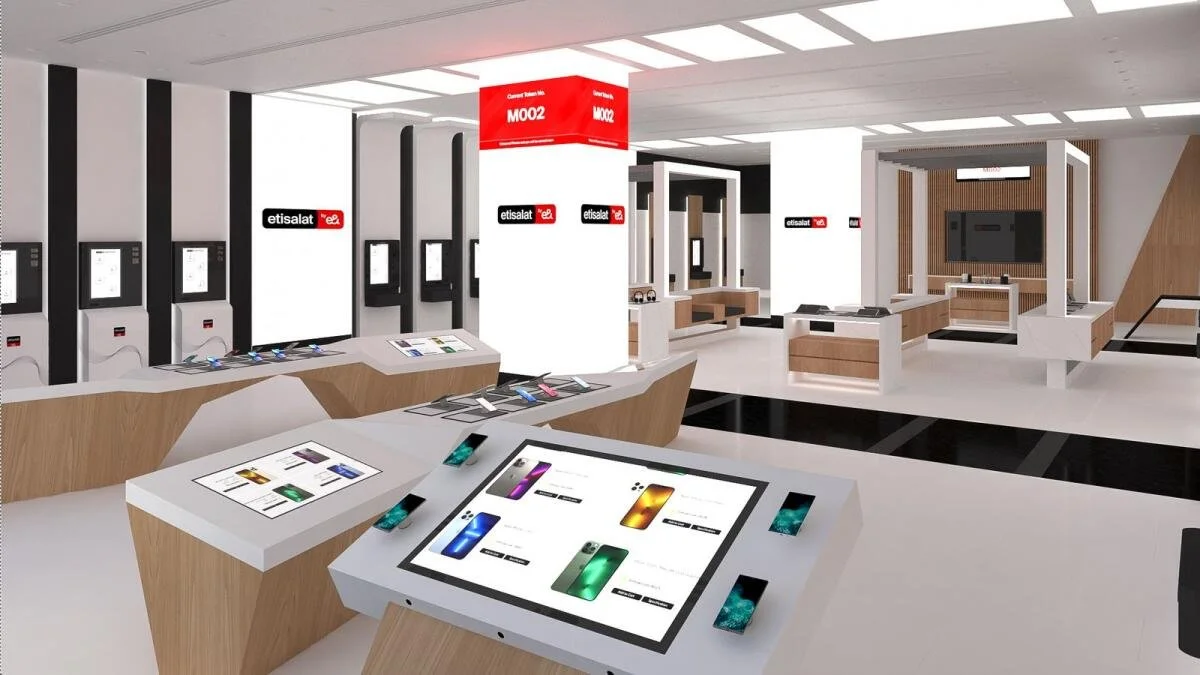
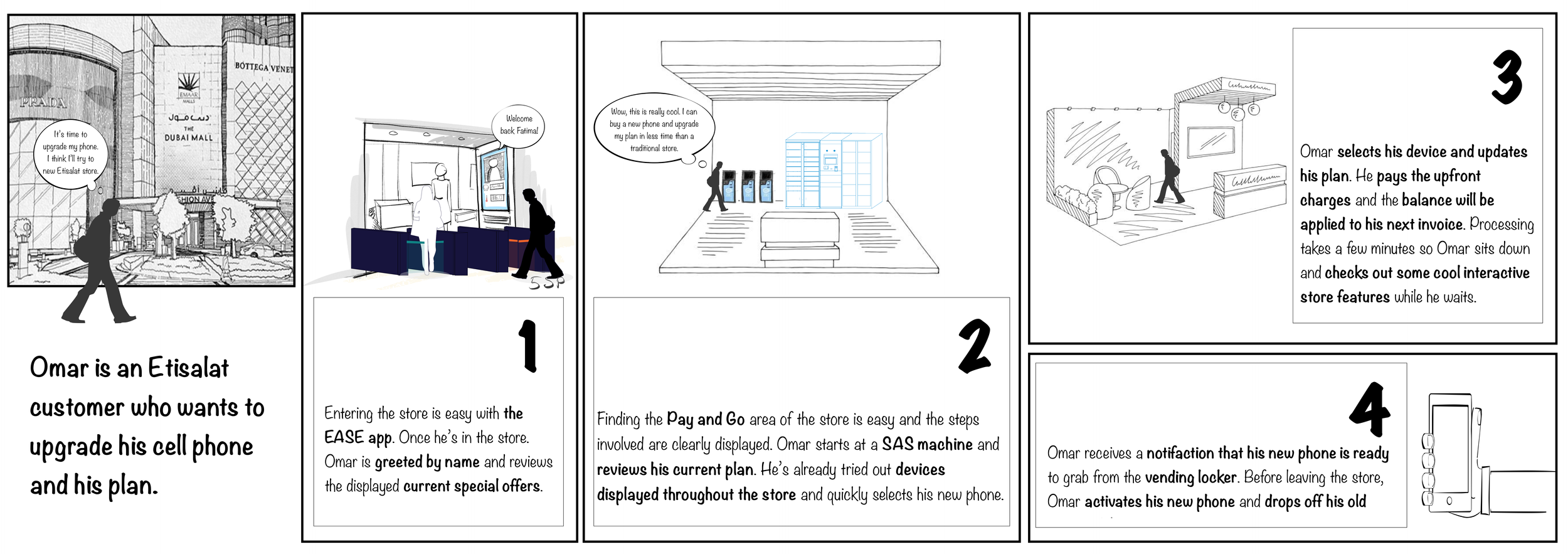
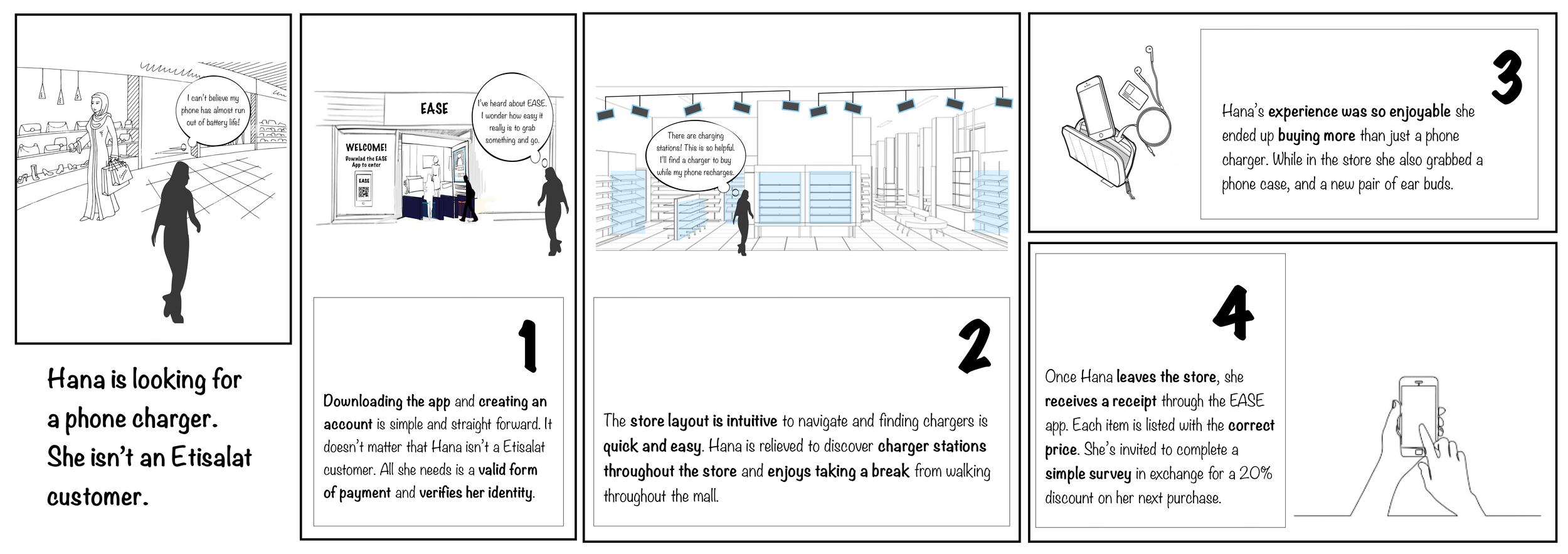
EASE Storyboards
One of my contributions was facilitating alignment across the project team to conceptualize the in-store experience, which included wayfinding and how customers would interact with the digital and physical environment. As a team, we used these concepts to work through potential points of friction and the possible lack of intuitive self-service. Before settling on hardware vendors, we collaborated with Etisalat’s EASE team to determine what capabilities met their requirements, including security compliance and safety.
Scenario 1: An existing customer needs to upgrade his cell phone and service plan.
Scenario 2: A non-customer needs to buy a phone accessory.
Service Design
The team used the store mockups I designed to establish a shared mental model of the total multi-experience (MX).
My contributions helped define the service blueprint, which was invaluable for the team. It allowed us to think through technical scenarios, customer requirements, and business use cases.
Edward Li designed the EASE service blueprint based on the direction provided by SMEs and myself.
A service blueprint for an autonomous retail store is a detailed visual document that maps out the entire service process, showing the interaction between customers, the store’s physical environment, and behind-the-scenes operations. This blueprint helps understand, analyze, and improve the customer experience and operational efficiency.
3. Backstage (Invisible) Actions
These are the behind-the-scenes activities that support frontstage actions but are not visible to customers. In an autonomous retail store, these might include:
Inventory management systems updating stock levels in real-time.
Data processing and analysis to personalize customer experiences.
Maintenance of autonomous systems like robots and sensors.
4. Support Processes
These are internal processes and systems that enable both frontstage and backstage actions. For an autonomous retail store, support processes might involve:
IT support for maintaining the store’s software and hardware infrastructure.
Logistics and supply chain management to ensure timely restocking of products.
Data security measures to protect customer information.
5. Physical Evidence
This includes all the tangible elements that customers encounter during their experience. For an autonomous retail store, physical evidence can include:
Store layout and design.
Signage and instructions for using autonomous systems.
Packaging and product displays.
Service Blueprint Components
1. Customer Actions
Customers take these steps when interacting with the store, such as entering the store, browsing products, selecting items, and making a purchase. In an autonomous retail store, this might include:
Entering the store using an app or QR code.
Browsing and selecting items using smart shelves.
Self-checkout using automated payment systems.
2. Frontstage (Visible) Actions
These are the actions and interactions that are visible to customers. For an autonomous retail store, frontstage actions include:
Interaction with digital displays or kiosks.
Assistance from robotic helpers or virtual assistants.
Automated checkout processes and payment systems.
Employee Training
+ Support Program
As part of my documentation responsibilities, I specified the store operation training material and post-implementation support during the pilot period. Using AI, the EASE pilot team continuously analyzes problems that arise and resolves any required changes following the rollout.
RFP Response Team: Amdocs Experience Division
-
Jessica Lowry
STRATEGY DIRECTOR
-
Edward Li
SERVICE DESIGNER
-
Laura Ruffino
SALES DIRECTOR, EXPERIENCE DIVISION
-
Mike Mannis
PROGRAM DIRECTOR
-
Gregory Leytman
HEAD OF DIGITAL ENGINEERING
-
Alex Kishinevsky
TECHNICAL DIRECTOR
PHOTO CREDIT: Martech Vibe Magazine, e& Launches AI-powered Autonomous Telecom Store
Amdocs’ solution comprises EASE store hardware, supporting software, and an Amdocs Integration layer (AIL) to connect EASE store components and the Etisalat ecosystem.
PHOTO CREDIT: Produced by Etisalat, Published by Gulf News
The Ease autonomous self-service store extends AI possibilities to some of e&'s consumer-facing services.
etisalat by e& Selects Amdocs to Revolutionize its In-Store Retail Experience with One of the World’s First AI-enabled Telco Autonomous Stores
Seamless and simplified end-to-end in-store shopping experience orchestrated and developed by etisalat by e& in collaboration with Amdocs and co-developed by Trigo; purpose-built app for the autonomous stores, ecosystem integration, and operations oversight ensure a personalized next-gen experience for customers
GITEX Global 2023
DUBAI, 21st October 2023 (WAM) -- e& successfully wrapped up its participation at GITEX Global 2023, attracting visitors, decision-makers, technology experts, and the media to its stand with a wide array of innovative use cases reflecting this year’s theme ‘Accelerating Innovation’.
A major announcement at the global technology event was the launch of ‘EASE’ (Etisalat by e& Autonomous Store Experience), the world’s first autonomous telecom store powered by AI. It utilizes ground-breaking technologies to empower customers to purchase e& products and services seamlessly.